Multi-Center Clinical Study on Protein C Project Jointly Conducted by Three Leading Hospitals
-
2025-08-28
-
Company News
Recently, a multi-center clinical study for Shanghai Sun Biotech Co., Ltd.'s Protein C Assay Kit (Chromogenic Substrate Method) has been successfully completed. Led by Peking University People's Hospital, with participation from the Institute of Hematology & Blood Diseases Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, and Zhujiang Hospital of Southern Medical University, this rigorous clinical validation spanning nearly 6 months demonstrated high equivalence in detection performance compared to imported reference reagents, achieving a correlation coefficient of 0.9942. This provides robust data support for the clinical application of domestic protein C detection reagents.
Authoritative Hospital Joint Validation
This clinical study was rigorously designed and implemented according to the "Technical Guidelines for Clinical Trials of In Vitro Diagnostic Reagents." All three participating institutions are leading hospitals in China's thrombosis and hemostasis diagnostic field. Peking University People's Hospital, serving as the coordinating center, is the National Clinical Medical Research Center for hematological diseases and houses the world's largest allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation center. With significant influence in establishing blood disease diagnostic standards, it undertook the overall coordination of this multi-center study. The Institute of Hematology & Blood Diseases Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, serves as the coordinating unit for the National Hemophilia Case Information Management and Treatment Collaboration Network and houses a national-level thrombosis and hemostasis diagnostic center. Its affiliated State Key Laboratory of Experimental Hematology has achieved remarkable results in coagulation molecular mechanism research. Zhujiang Hospital of Southern Medical University represents top-tier clinical laboratory standards in South China, with its hematology department designated as a national pediatric blood disease treatment center, demonstrating outstanding advantages in thrombotic disease diagnosis and treatment. The authoritative status and geographical representativeness of these three hospitals provided rigorous technical support and reliable data diversity assurance for this study, ensuring the scientific validity and reliability of the multi-center research.
Rigorous Multi-Center Study Confirms Equivalence with Imported Reagents
The study screened 859 plasma samples, all successfully enrolled and included in the full analysis set. After sample exclusion, 805 valid samples were ultimately included in the per-protocol set for statistical analysis. The sample population showed broad age distribution, ranging from 1 to 92 years with a mean age of 47.0 years, and balanced gender ratio (58.6%:41.4%), fully reflecting real-world clinical application scenarios. This wide age distribution and balanced gender ratio ensured the universal applicability of study results across different populations.
The Pearson correlation coefficient is a core indicator for evaluating the correlation between two detection methods, with coefficients closer to 1 indicating higher linear correlation between methods. In this study, the Pearson correlation coefficient between test reagent and imported reference reagent reached 0.9942, further improving to 0.9952 after outlier removal, with p-values all less than 0.0001, indicating extremely high correlation between the two reagents' detection results.
Passing-Bablok regression is a non-parametric linear regression method used to compare consistency between two detection methods. The Passing-Bablok regression analysis in this study showed a regression equation slope b = 1.0333 (95% CI: 1.0263-1.0408), and intercept a = -0.0333 (95% CI: -0.5918 to 0.4474). The regression equation slope approaches 1, with the lower limit of the 95% confidence interval exceeding 0.9, and the intercept approaches 0, confirming high consistency between the test reagent and imported reference reagent across the entire detection range.
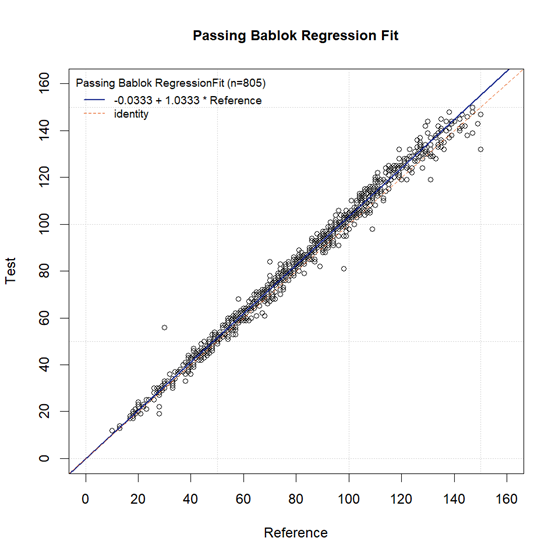
Passing-Bablok Regression Plot of Test Reagent and Reference Reagent Detection Results
Guidelines and Consensus Recommendations for Multi-Disciplinary Protein C Testing Applications
Protein C is an important anticoagulant factor, and its deficiency is the most common type of hereditary thrombophilia in China. Protein C testing holds significant importance for diagnosing thrombotic diseases and monitoring anticoagulation therapy. The "Chinese Guidelines for Diagnosis and Prevention of Thrombophilia (2021)" clearly recommends protein C activity testing as one of the core laboratory indicators for thrombophilia etiology screening and diagnosis.
For warfarin anticoagulation therapy monitoring, the "Chinese Guidelines for Diagnosis and Prevention of Thrombophilia (2021)" suggests that patients with protein C and protein S deficiency cannot use warfarin or other coumarin anticoagulants as initial anticoagulation therapy, as this may cause worsening thrombotic tendency and skin necrosis [1A]. The "Chinese Expert Consensus on Warfarin Anticoagulation Therapy (2013)" indicates that rare but serious adverse reactions such as acute thrombosis and skin necrosis during warfarin treatment are usually related to protein C and protein S deficiency.
Additionally, the "Guidelines for thrombophilia testing: A British Society for Haematology guideline" recommends urgent testing for protein C and S deficiency in neonates and children with purpura fulminans (Grade 1B). The "EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Vascular diseases of the liver (2015)" suggests that thrombophilia screening should include protein C level testing. Multiple expert guidelines and consensus documents including the "Chinese Expert Consensus on Natural Abortion Diagnosis and Treatment (2020)," "Guidelines for Prevention and Treatment of Tumor-Associated Venous Thromboembolism (2019)," and "Chinese Expert Consensus on Application of Anticoagulation Technology in Critical Care Renal Replacement Therapy (2023 Edition)" all list protein C testing as an important laboratory indicator, confirming the broad application value of protein C across multiple clinical departments including hematology, laboratory medicine, obstetrics and gynecology, oncology, and ICU.
The completion of Shanghai Sunbio's multi-center clinical study demonstrates that the company's protein C detection kit can fully meet clinical testing requirements, providing laboratories with a reliable domestic alternative.

In the current context of medical cost control, selecting reliable and cost-effective domestic products aligns with national policy guidance and benefits sustainable hospital development. The multi-center clinical study results confirm the equivalence of the company's protein C detection kit with imported products, providing clinical data support for laboratory product replacement decisions. The company will continue dedicating itself to the research and development of high-quality coagulation testing products, making greater contributions to China's laboratory medicine development and public health protection.